Converting PowerShell Task in YAML
YAML Builds have many advantages over traditional build definitions, especially because YAML build definitions follows branching of code , a killer feature that is fantastic if you use GitFlow.
YAML Build definitions are stored in code, this allows them to follow branches, minimizing the need to maintain builds that should build code in different moment in time.
As an example I have a build where I have tasks to publish some Web Sites, if I had a new Web Site to publish, I can add another task in YAML build, but the build still work for older branches, especially for the master branch that represent my code in production.
To minimize impacts, I tend to use PowerShell scripts stored inside code repository to perform build tasks, this was an old trick useful when YAML build was not present. Scripts allows you to create a generic build, add some tasks to run PowerShell scripts, and the result is that scripts follow branches.
Now that YAML Build is available, I started converting everything to YAML build, a task that is made simple tanks to a nice feature of VSTS, in the UI there is a nice View YAML button that convert all of my build definition with new YAML syntax.
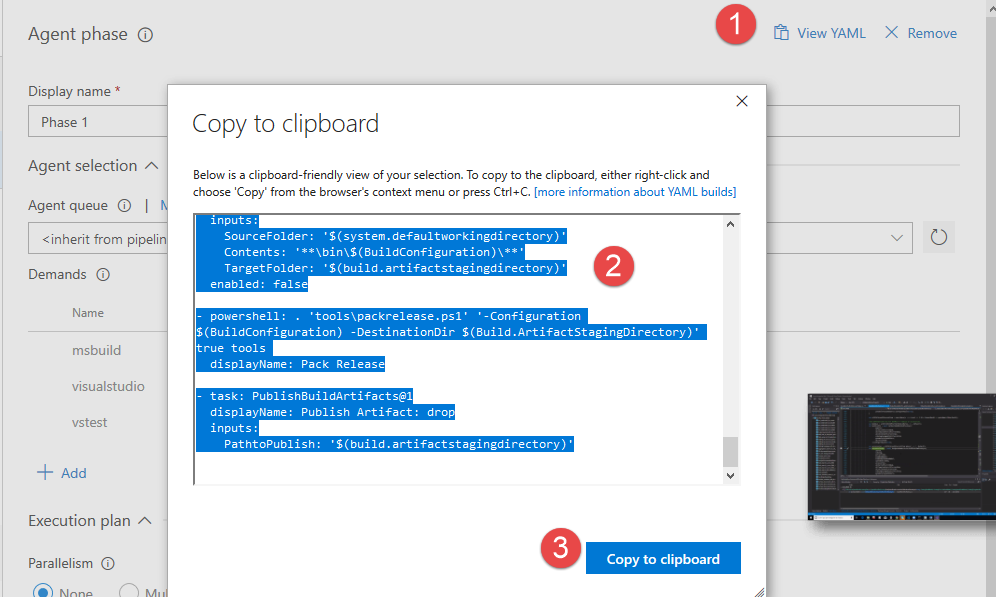
Figure 1: Ui functionality to show the current standard build definition translated to new YAML build definition.
As you can see from Figure 1, PowerShell tasks is not converted as a task, but with a node of type powershell, followed by parameters. This is perfectly valid, because YAML build can contain a powershell node, but in my specific situation the build failed, because the conversion failed to setup working directory.
Even if YAML build allows direct call of PowerShell scripts, if you convert a working build that uses PowerShell task it is better to use the same Task inside YAML definition.
To solve my problem I simply changed generated YAML build definition to use a standard PowerShell task, this is the declaration of the task.
| |
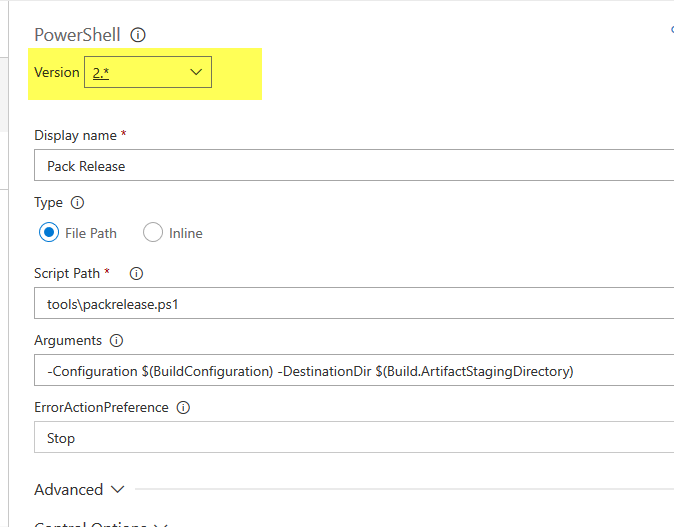
As usual you specify a task and the type, in this example PowerShell@2. It is important the version after the @ character, it should be equal to the version of the task in the standard build, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Pay attention to version Task when you convert to YAML build.
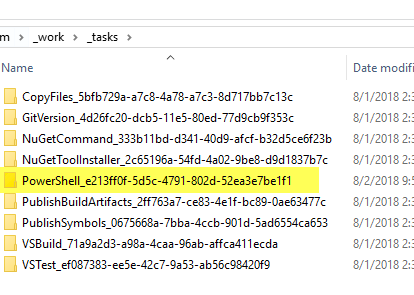
To know input parameter name of the tasks (Es. targetType, arguments, workingDirectory, etc), the most immediate solution is looking in the working directory of an agent and find the task definition.
Figure 3: Tasks inside working folder of an agent.
Inside the folder of the chosen task there are all latest version for any major version, and inside each version folder there is a task.json file that can be inspected to know the exact version of the parameter.
After modifying YAML build to use PowerShell task the build started working as usual.
Gian Maria.