Local workspaces in TFS11
The concept of Workspace is a key point in Team Foundation Server, it represents the mapping between a local version and server version of source control of a Team Project. The Workspace model of TFS was somewhat criticized in the past, because it is logically Server Side, because TFS Server, in each moment, knows the situation of each workspace.
This choice has, (as any choice in real life :) ) good and bad point. The good point is that Get Latest operation are really quick, because the server knows the situation of your workspace and can simply send you all files that were modified since the previous Get operation. The bad part is that, if you delete a file from windows explorer, when you issue a Get Latest it is not downloaded again, because the server really believe that the file is in your workspace (you can solve such inconsistencies with* tfpt scorch *command from power tools). Another annoying problem is that all files are read-only on disk, because before starting a file modification you should contact the server to do a Check-Out operation. This does not mean that the file is locked, just that you need to make the server knows the fact that you started modifying that file.
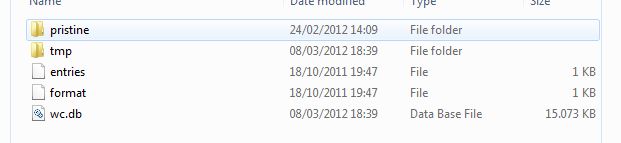
On the contrary, subversion uses a different type of mapping, based only on local version of files. A local folder mapped to a subversion repository contains a special folder called * .svn *, where subversion stores lots of information about the situation of the local mapping of the sources
Figure 1: Screenshot of a.svn folder of subversion repository
In previous subversion mapping structure (it was changed last year), you have a.svn folder for each subfolder of your local copies of the sources.
With such a structure if you delete a file and issue an *Update,*client component of subversion scans the directory, find the differencies from the server version, verify that a file is missing and restore it from the server version. All files are not readonly, because you can simply open notepad and edit a file. When it is time to Commitmodification to server, the client component of subversions simply checks all files that are different from the latest update and consider them to be candidate to be updated on the server.
This approach is good until you start to have huge repository, not only because the.svn folder contains the copies of all the file, but because each update or commit operation actually scans all folders to understand what to do. I have a big project in subversion where the first update operation of the trunk needs about a couple of minutes on a computer with a standard 7.200 RPM disk and about 2 seconds on my Vertex 3 SSD. This demonstrates how huge is the Disk Activity with such a mapping model of your source control.
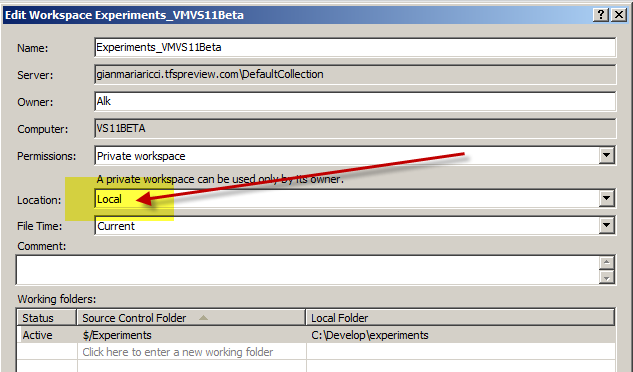
Luckily enough, we have now really good SSD at very low price and disk activity is not a problem anymore, so be happy to know that in TFS11 a new version of workspace was introduced, called Local Workspace, and this is actually the default workspace model in TFS11.
Figure 2: Local workspace in action.
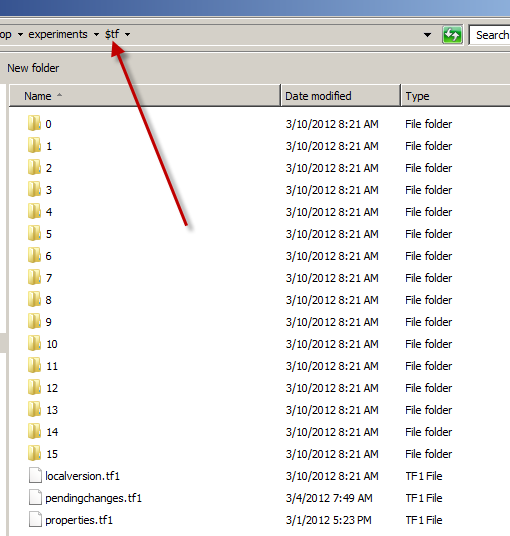
A local workspace is really similar to a subversion workspace, it has a $tf hidden folder that contains information on the local workspace.
Figure 3: The $tf folder in a local workspace
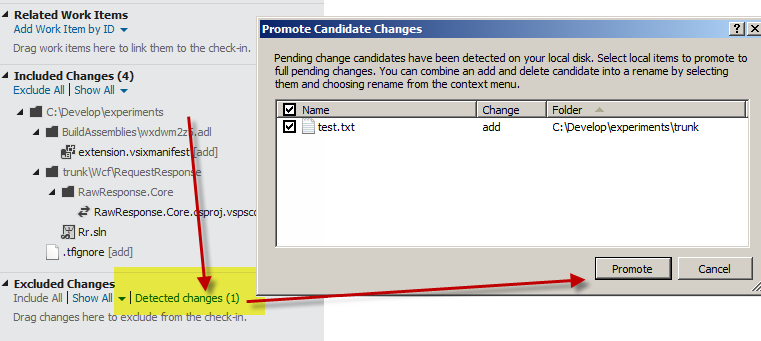
You can add a file outside Visual Studio, and during check-in operation you will find detected changes in Team Explorer
Figure 4: Detected changes during a check-in operation
This means that VS is able to recognize files that were added outside VS, simplifying a lot offline operations.
Gian Maria